Aging is a natural biological process that affects all tissues and organs in the body. One of the most common age-related conditions is osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Osteoarthritis causes pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the affected joints. This blog section will provide an overview of aging and osteoarthritis, and how aging affects the body's joints.
Overview of aging and osteoarthritis
Aging is a complex process that involves cellular and molecular changes throughout the body. As people age, the body's ability to repair and maintain tissues and organs gradually declines, leading to the development of age-related conditions such as osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is a progressive joint disease that mainly affects the knee, hip, and hand joints. The condition is characterized by the breakdown and loss of cartilage, a cushioning tissue that covers the joints' ends, causing bones to rub against each other, resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness, and eventually, joint damage.
How aging affects the body's joints
Aging affects the body's joints in several ways. First, the production of synovial fluid, a lubricating fluid inside the joints, decreases with age, leading to reduced joint flexibility and mobility. Second, the cartilage that covers the joints' ends becomes thinner and less elastic, leading to increased friction between bones and further wear and tear. Third, the ligaments and tendons that hold the joints together become less elastic, making them more susceptible to tears and injuries. Finally, chronic inflammation, a common feature of aging, can damage joint tissues, exacerbating osteoarthritis symptoms.
In conclusion, aging is a complex biological process that affects all tissues and organs in the body, including the joints. Osteoarthritis is a prevalent age-related condition characterized by joint pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. Understanding how aging affects the body's joints is crucial in developing effective strategies to manage and treat osteoarthritis.

Understanding Osteoarthritis
What is osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide, especially older adults. It is a chronic condition that primarily affects the weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine, as well as the hands and fingers. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage, the cushioning tissue that covers the ends of bones, breaks down over time, causing bones to rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
Causes and risk factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of osteoarthritis, including age, genetics, obesity, joint injury or trauma, and repetitive use of joints. As individuals age, the body's ability to repair and maintain tissues reduces, predisposing them to osteoarthritis. Genetics also play a role in osteoarthritis development, with some people more prone to the disease due to inherited traits. Obesity increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis by placing excess weight on the joints, leading to accelerated wear and tear. Joint injuries or trauma, such as those that occur during sports, can damage the joint's structure, also increasing the risk of developing osteoarthritis. Lastly, the repetitive use of joints in occupations or sports that involve repetitive motions can lead to the breakdown of the cartilage cushioning the joints.
In conclusion, understanding osteoarthritis's causes and risk factors is essential in managing and preventing the development of the disease. Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, several treatment options, such as physical therapy, weight management, and medications, can help alleviate symptoms and improve joint function.
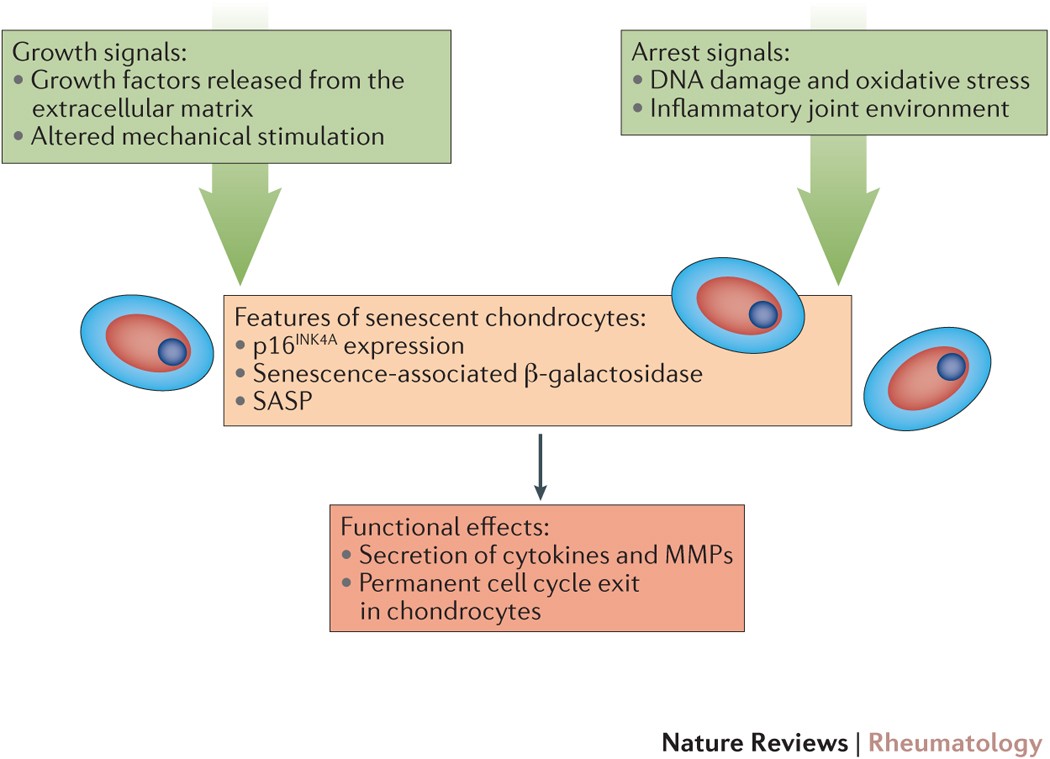
Signs and Symptoms
Common symptoms of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. The most common symptoms of osteoarthritis include pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility of joints. People with osteoarthritis often experience increased pain and stiffness in their joints in the morning, after prolonged inactivity, or after rigorous activity. The affected joint area may also be swollen, tender, or warm to the touch. Moreover, as the disease progresses, bones may form spurs around the affected joint, restricting movement and causing further pain.
How to recognize the signs
Recognizing the signs of osteoarthritis is essential in managing the condition. Common signs and symptoms include pain and stiffness in the joints, especially after periods of inactivity. People with osteoarthritis may also experience clicking or cracking sounds when moving the affected joint, which indicates damaged cartilage rubbing against the bones. Furthermore, swelling and tenderness around the affected joint area are common in osteoarthritis cases. If left untreated, people with osteoarthritis may experience reduced mobility and an increased risk of developing other conditions, such as depression or anxiety.
It is crucial to consult a doctor when experiencing persistent joint pain and stiffness or have difficulty moving the joints. Early diagnosis and treatment can help decrease the severity of symptoms and improve overall joint function. In conclusion, understanding the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis is essential in managing the disease effectively.
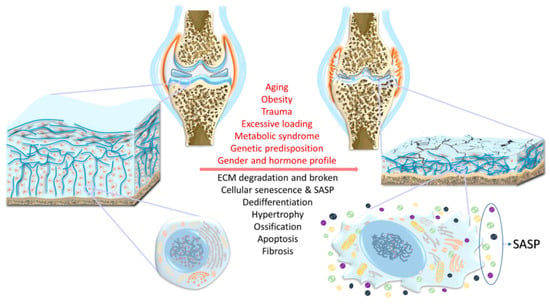
Diagnosis and Treatment Strategies
How is osteoarthritis diagnosed?
To diagnose osteoarthritis, a doctor typically starts with a physical examination of the patient and asks about their medical history. The doctor may also request imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to check for signs of joint damage or bone spurs. Blood tests are generally not used in diagnosing osteoarthritis, but they may be used to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms.
Treatment options available
There are various treatment options available for individuals with osteoarthritis, depending on the severity of symptoms. Common treatments include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and topical creams can help manage joint pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercise programs designed to help strengthen the affected joint and improve flexibility can also alleviate pain and stiffness.
- Joint injections: Injections of corticosteroids or lubricants can help reduce inflammation and improve joint mobility.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be needed to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle changes can also make a significant impact on managing osteoarthritis symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing proper joint protection techniques during physical activity, and incorporating low-impact exercise into daily routines are all recommended.
Overall, early diagnosis and treatment of osteoarthritis can help improve joint function and decrease the severity of symptoms. It is essential to consult a doctor when experiencing persistent joint pain or stiffness to receive an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
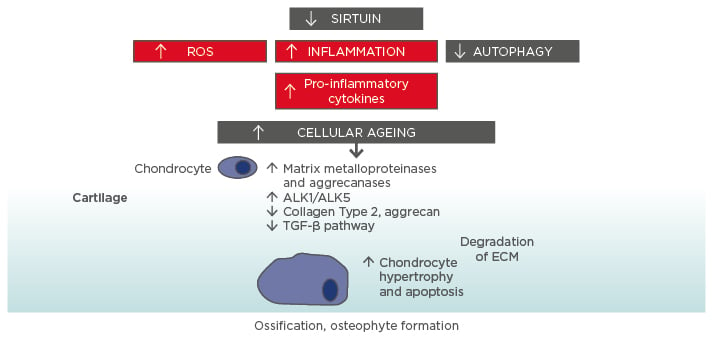
Exercise and Lifestyle Modifications
The role of exercise in osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide and is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. While it may seem counterintuitive, exercise can actually be an effective way to manage symptoms of osteoarthritis. Regular exercise helps to maintain joint mobility, strengthen muscles surrounding the affected joint, and reduce pain and stiffness.
Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for individuals with osteoarthritis as they are gentle on the joints but still provide cardiovascular benefits. Strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance bands, can help improve overall muscle tone and protect the joints from further damage. Range-of-motion exercises, such as stretching or yoga, can also help improve joint flexibility and reduce stiffness.
Lifestyle changes to manage symptoms
In addition to exercise, certain lifestyle modifications can also help manage symptoms of osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial as excess weight can put additional stress on the joints, leading to further damage. A healthy diet that is rich in nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids can also help to support joint health.
Individuals with osteoarthritis should also practice proper joint protection techniques during physical activity. This may include wearing supportive shoes, using assistive devices like canes or braces, and avoiding activities that put unnecessary strain on the joints. Finally, incorporating relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises can help to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
In conclusion, exercise and lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing symptoms of osteoarthritis. By incorporating low-impact exercise into daily routines, maintaining a healthy weight, and practicing proper joint protection techniques, individuals with osteoarthritis can improve joint function and reduce pain and stiffness. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen or making significant lifestyle changes.

