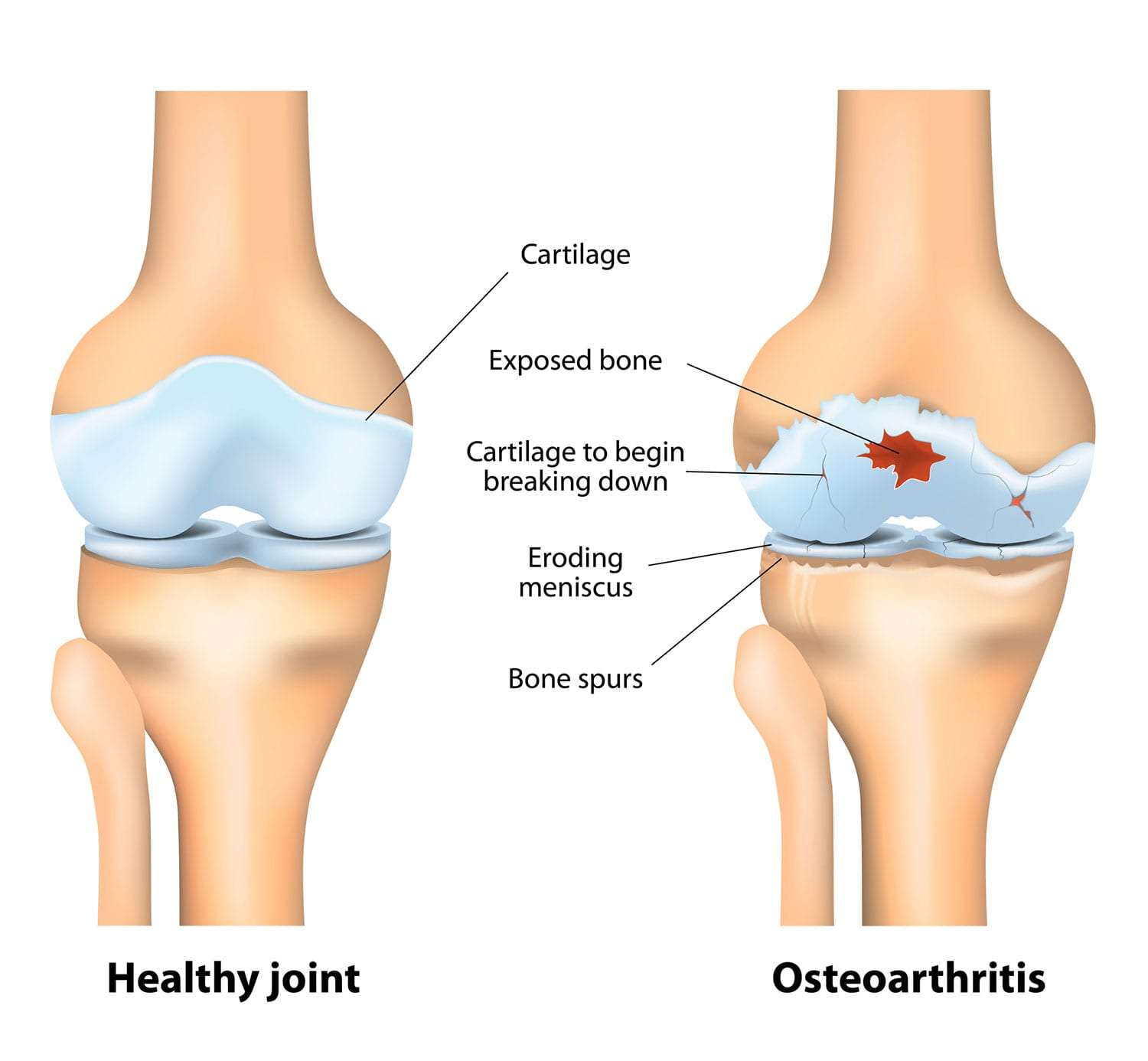
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis which affects the joints, causing them to become stiff, painful, and limiting daily activities. It is a chronic condition that typically worsens with age. Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, exercise can be an effective way to manage and reduce symptoms.

Explanation of Osteoarthritis and exercise:
Regular exercise can help increase strength and flexibility in the affected joints, reduce pain and stiffness, and improve overall physical function. Exercise can also help with weight management and improve cardiovascular health, which can help reduce the risk of other chronic diseases. However, it is important to note that not all types of exercise are beneficial for those with osteoarthritis.
Low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, and cycling are typically recommended for those with osteoarthritis. These exercises can help reduce stress on the affected joints while still providing cardiovascular benefits. Strengthening exercises such as resistance training and yoga can also be beneficial in improving joint stability and reducing pain.
It is also important to engage in regular physical activity and avoid prolonged periods of sitting or inactivity. Even small amounts of movement throughout the day can provide benefits for those with osteoarthritis. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or certified exercise specialist before beginning any new exercise program.
Overall, exercise can be an effective way to manage and reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis. By incorporating regular physical activity into their daily routine, those with osteoarthritis can improve their quality of life and reduce their risk of other chronic conditions.

Benefits of Exercise for Osteoarthritis
Why exercise helps Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis that specifically affects the joints, leading to stiffness, pain, and limitations in daily activities. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, regular exercise has been shown to manage and reduce symptoms. Exercise helps increase flexibility and strength of affected joints, reduces pain and stiffness, and improves overall physical function. It can also help with weight management and improve cardiovascular health, which reduces the risk of other chronic diseases.
Understanding Bone and Joint Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Hip replacement: A surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one
Promising Research and Developments for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Children: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overcoming Fatigue and Depression Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Relationship Between Diet and Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
When to Seek Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Key Differences Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Coping Strategies and Treatment Options
Understanding the Symptoms and Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Discussion on pain relief and improved mobility
Low-impact exercises such as walking, cycling, and swimming are great for those with osteoarthritis as they reduce pressure on the affected joints while providing cardiovascular benefits. Resistance training and yoga can also relieve pain, increase joint stability, flexibility, mobility and overall function, reducing reliance on medication. Regular physical activity, even in small amounts, is beneficial for those with osteoarthritis, as it helps keep the senses active. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or certified exercise specialist before beginning any new exercise program. Overall, regular exercise can significantly improve the quality of life for those with osteoarthritis by reducing symptoms and improving overall health.

Talk to Your Doctor
Consult your doctor before starting exercise
It is important to include exercises in the daily routine for managing osteoarthritis, but it is equally important to talk to a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program. Depending on the severity and type of osteoarthritis, the exercise routine may vary to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Working with a professional
Consulting with a certified exercise specialist or physical therapist can help in developing an exercise program that fits individual needs, including activities like aerobic exercises, strength training, and range of motion exercises. A healthcare professional may also monitor progress to ensure the success of the exercise program.
Implementation of exercise programs may require some adaptations, like modifications in intensity and joint range of motion, to accommodate special needs. In addition, exercise must be done alongside medications and other therapies especially when conditions are severe.
Finally, it is important to listen to and respect the body as the individual progresses into an exercise routine to prevent injury or overuse. Exercise is an essential part of managing osteoarthritis, but only when done safely and properly. By working with a healthcare professional, individuals with osteoarthritis can reap the benefits of exercise while minimizing the risk of complications or injury.

Types of Exercise for Osteoarthritis
Types of exercises recommended
To help manage osteoarthritis, regular exercise is recommended, which helps with pain relief and increased mobility. The Arthritis Foundation suggests a variety of exercises that can be beneficial to people with osteoarthritis, including:
- Aerobic exercises, such as walking, swimming, or cycling to increase cardiovascular fitness.
- Strength training, which involves lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises to build muscle strength.
- Stretching, which increases flexibility and range of motion.
- Balance exercises, which can reduce the risk of falls.
Low-Impact and Range of Motion Exercises
Low-impact exercises, such as walking or cycling, are often recommended for people with osteoarthritis since they put less stress on the joints. Range of motion exercises, such as yoga or tai chi, are also recommended as they maintain flexibility and reduce stiffness. Combining low-impact exercises with range of motion exercises can be an effective way to manage osteoarthritis and prevent further damage to the joints.
It is important to note that exercise routines should be tailored based on individual needs and symptoms. It is also recommended to maintain a regular exercise routine and to start slowly, gradually increasing intensity and duration over time. By incorporating regular exercise into daily routines, individuals with osteoarthritis can improve their overall quality of life and reduce pain and stiffness in their joints.
Types of Exercise for Osteoarthritis
Regular exercise can play a significant role in managing osteoarthritis. It can help with pain relief, increase mobility, and improve overall health. There are different types of exercises recommended by the Arthritis Foundation that can benefit people with osteoarthritis. These exercises include aerobic exercises, strength training, stretching, and balance exercises.
Low-Impact and Range of Motion Exercises
Low-impact exercises like walking and cycling and range of motion exercises such as yoga and tai chi are considered beneficial for people with osteoarthritis. These exercises put less stress on the joints and maintain flexibility, reduce stiffness and build muscle around the joints to protect them from further damage. By combining low-impact exercises with range of motion exercises, people with osteoarthritis can improve their joint mobility and overall health.
However, it is important to note that exercise routines should be tailored to each individual's needs and symptoms. It is recommended to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of exercise over time. Maintaining a regular exercise routine is essential to managing osteoarthritis effectively.
Strength Training
Building muscle around the joints is crucial in managing osteoarthritis. Strength training involves lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises to build muscle strength. It improves balance, reduces the risk of falls and strengthens bones. Resistance and endurance training are two types of strength training recommended for people with osteoarthritis.
In summary, incorporating regular exercise into daily routines such as aerobic exercises, strength training, stretching, balance exercises, low-impact and range of motion exercises can help manage osteoarthritis. Building muscle around the joints through resistance and endurance training is also highly recommended. Tailored exercise routines, consistent practice, and gradual progress can significantly improve the quality of life for people with osteoarthritis.

Types of Exercise for Managing Osteoarthritis
Regular exercise is essential in managing osteoarthritis to improve joint mobility, reduce stiffness, and protect the joints from further damage. The Arthritis Foundation recommends various types of exercises that can benefit people with osteoarthritis, including aerobic exercises, strength training, stretching, balance exercises, low-impact and range of motion exercises.
Low-Impact and Range of Motion Exercises
Low-impact exercises like walking and cycling, and range of motion exercises such as yoga and tai chi are excellent choices for people with osteoarthritis. These exercises put less stress on the joints and aid in maintaining joint flexibility, decreasing stiffness and building muscle around the joints. Combining low-impact exercises with range of motion exercises can significantly improve joint mobility and overall health for individuals with osteoarthritis.
Strength Training
Building muscles around the joints is crucial for managing osteoarthritis. Strength training involves lifting weights or doing bodyweight exercises to strengthen the muscles. It improves balance, decreases the risk of falls, and strengthens bones. Resistance and endurance training are two types of strength training recommended for people with osteoarthritis.
Flexibility Training
Flexibility training improves joint mobility and decreases stiffness. It involves stretching exercises that help the joints to move freely. People with osteoarthritis can benefit from various types of flexibility techniques such as static, dynamic, and active stretching. It is important to note that flexibility exercises should be performed correctly to avoid injury.
In conclusion, regular exercise is a crucial part of managing osteoarthritis effectively. Aerobic exercises, strength training, stretching, balance exercises, low-impact exercises, range of motion exercises, and flexibility training can provide benefits to individuals with osteoarthritis. Understanding the types of exercises and incorporating them into daily routines can significantly improve the quality of life for people with osteoarthritis.

.jpg)