Introduction:
Osteoarthritis is a silent pain epidemic that affects millions of people around the world. This condition is caused by the wear and tear of the joints, leading to stiffness, pain, and limited mobility. It is more common among older adults, but it can also affect younger individuals who engage in high-impact activities or have a family history of the condition.
Overview of Osteoarthritis as a Silent Pain Epidemic:
According to research, osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, and it affects approximately 302 million people worldwide. In the United States alone, it affects over 32.5 million adults, which is 13.2% of the total population. It is also one of the leading causes of disability, affecting the quality of life of those who suffer from it.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition that affects the joints, causing them to break down over time. The most commonly affected joints include the knees, hips, and hands. Symptoms may include pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited mobility. These symptoms can worsen over time, making it difficult for individuals to perform their daily activities and even go to work.
Risk factors for osteoarthritis include age, gender, genetics, obesity, joint injuries, and repetitive stress on the joints. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are several treatments available to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for those who suffer from it.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a silent pain epidemic that affects millions of people worldwide, causing them to experience a diminished quality of life. With the right treatment and management, individuals with osteoarthritis can manage their symptoms and continue living a fulfilling life.

Introduction:
Osteoarthritis is a widespread degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people across the globe. This chronic condition is caused by the wearing down of cartilage, the soft tissue that cushions the joints. Without this cushion, the bones in the joint grind against each other, causing pain, swelling, and loss of function. Osteoarthritis can occur in any joint, but it often affects the hips, knees, hands, and spine.
Overview of Osteoarthritis as a Silent Pain Epidemic:
Despite its prevalence and debilitating effects, osteoarthritis often goes unnoticed and untreated. It has been referred to as a silent pain epidemic due to its insidious onset and the gradual progression of symptoms. Osteoarthritis can take years to develop, and symptoms may initially be mild and intermittent. Many people are not aware they have the condition until it has progressed to the point that it affects their daily activities and quality of life.
Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults, but it can affect people of all ages. Risk factors include obesity, joint injuries, and genetic predisposition. Women are also more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men. While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are treatments available to manage symptoms and slow the progression of the disease.
Comparing different treatments for osteoarthritis, there are several options, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery. Each treatment has its own benefits and drawbacks, and the choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition, the individual's health status and preferences, and other factors.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a significant healthcare issue that affects a large proportion of the population. While the disease can be debilitating, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected.

Osteoarthritis: Understanding the Basics
Osteoarthritis Definition
Osteoarthritis is a chronic degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. It is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, the soft tissue that protects and cushions the bones in a joint. When cartilage wears down, the bones in the joint rub against each other, causing pain, stiffness, swelling, and loss of function. Osteoarthritis can impact any joint, but it most commonly affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Causes of Osteoarthritis
Age is a significant risk factor for developing osteoarthritis, but it can affect people of all ages. Other factors include joint injuries, obesity, and genetic predisposition. Women are more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men. Despite its prevalence, osteoarthritis is often unnoticed and untreated, earning it the title of “silent pain epidemic”. It has a gradual onset and progression of symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose in the early stages.
Comparison of Osteoarthritis Treatments
There are several options for treating osteoarthritis, including medication, physical therapy, and surgery. Each treatment has advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of treatment depends on several factors, such as disease severity, the individual's health status and lifestyle, and personal preference. Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a prevalent and significant healthcare issue that affects a vast percentage of the general population. Understanding the basics of this chronic condition, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is essential. Osteoarthritis treatment options must be individualized to achieve the best outcomes for each person experiencing the condition.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Common Symptoms
Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that affects the joints. Its symptoms may start off mild and gradually worsen over time. The most common symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
- Pain in the affected joint
- Stiffness in the affected joint, particularly after sleeping or sitting for long periods
- Creaking or cracking sounds from the affected joint during movement
- Tenderness or swelling around the affected joint
- Loss of flexibility in the affected joint
Severity of symptoms
The severity of symptoms in people with osteoarthritis can vary widely. Some individuals may experience mild pain and stiffness, while others may have severe symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life. Factors that determine the severity of symptoms include age, gender, genetics, and the extent of joint damage. In general, symptoms of osteoarthritis tend to worsen over time, especially if the disease is left untreated.
It's important to remember that early detection and treatment of osteoarthritis can help prevent symptoms from worsening and improve outcomes. If you're experiencing symptoms of osteoarthritis, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.

Understanding Bone and Joint Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Hip replacement: A surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one
Promising Research and Developments for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Children: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overcoming Fatigue and Depression Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Relationship Between Diet and Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
When to Seek Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Key Differences Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Coping Strategies and Treatment Options
Understanding the Symptoms and Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis
Tests Used to Diagnose Osteoarthritis
To diagnose osteoarthritis, healthcare professionals use a combination of methods. The most common approaches include medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests. During the medical history assessment, the healthcare provider will ask questions about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and family history. The physical exam typically involves examining the affected joint, looking for swelling, tenderness, or stiffness. Imaging tests that may be used to diagnose osteoarthritis include X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound.
When to seek medical attention
Individuals experiencing joint pain or stiffness that lasts for more than a few days should seek medical attention. Additionally, if symptoms get worse over time or interfere with daily activities, consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended. Early detection and treatment of osteoarthritis can help prevent further damage to the affected joint and improve symptom management. It's essential to remember that while mild symptoms may occur due to aging, ongoing or severe pain and stiffness should not be ignored and should prompt medical attention. Patients should discuss their treatment options and management plans with their healthcare provider, which could include lifestyle changes, physical therapy, or medication.

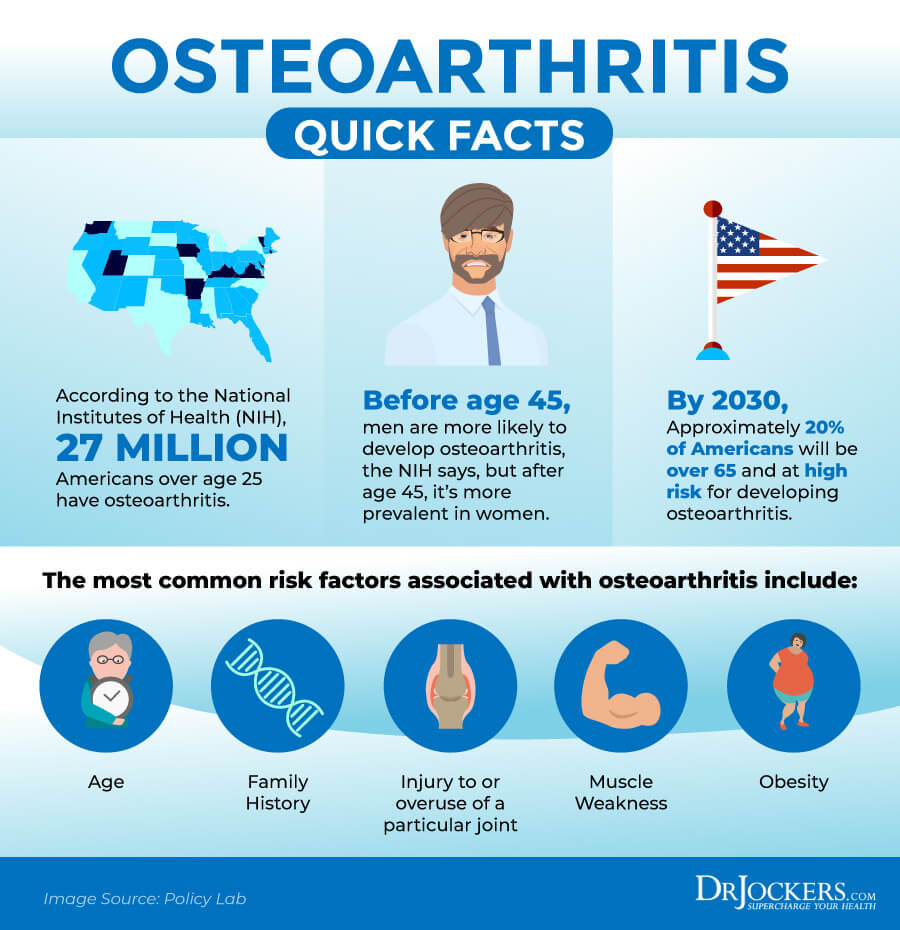
Risk Factors for Osteoarthritis
Contributing Factors of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Several factors contribute to the development of osteoarthritis, including age, gender, genetics, obesity, and injury. The condition occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the bones in the joint wears down over time, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. One of the key contributing factors is age, as the chances of developing osteoarthritis increase as a person gets older. Women are also more likely than men to have osteoarthritis, especially after menopause. Additionally, family history and genetics play a role, as some individuals may be predisposed to developing the condition due to their genes.
Effects of Osteoarthritis on daily life and routine
Osteoarthritis can have significant effects on a person's daily life and routines, depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced range of motion in the affected joint. As a result, individuals living with osteoarthritis may find it challenging to perform everyday tasks such as getting dressed, cooking, and cleaning. The condition can also interfere with work and recreational activities, leading to a decreased quality of life. Early detection and management are crucial to preventing further damage to the affected joint and improving symptom control. Healthcare professionals may recommend lifestyle changes, physical therapy, medications, and in severe cases, joint replacement surgery. Patients with osteoarthritis should discuss their treatment options with their healthcare providers to find a plan that suits their needs and goals.

Prevention and Treatment of Osteoarthritis
Prevention
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects many people worldwide. While there is no surefire way to prevent osteoarthritis, certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight is a good place to start, as carrying excess weight can put extra strain on joints and increase the likelihood of joint damage. Regular exercise that includes weight-bearing activities such as walking and strength training can help keep bones and joints healthy. It's also essential to avoid injuries that can damage joints, so it's vital to use proper protective equipment when playing sports or engaging in other physical activities. Lastly, individuals should maintain good posture and use proper ergonomics when sitting or standing for long periods of time.
Treatment
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, several treatments can help manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the condition. Treatment options include physical therapy, pain management medications, and surgery in severe cases. Physical therapy can help strengthen muscles around affected joints, leading to less pain and improved mobility. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help manage pain and inflammation. Injections of corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid into the affected joint can also provide relief. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one. It's essential to discuss treatment options with a healthcare provider to find the best plan for managing osteoarthritis symptoms.

